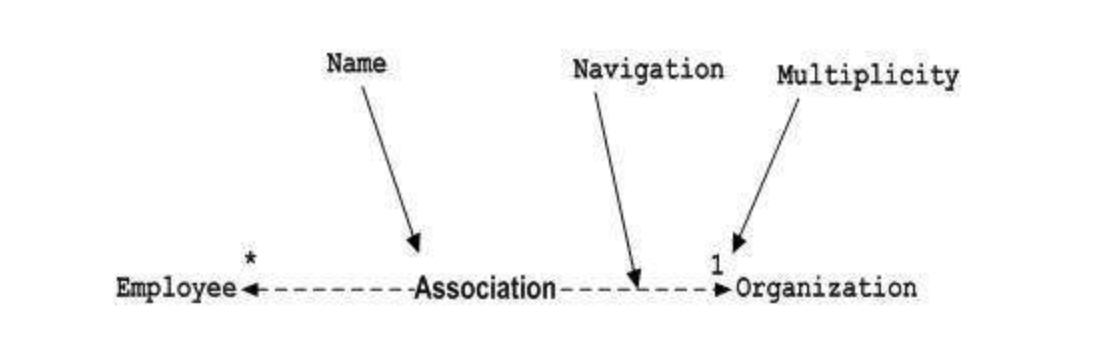
Associations
They define how entities are related and interact with each other within the problem domain.
One-to-One (1:1) Association:
- In a one-to-one association, one instance of an entity is directly related to exactly one instance of another entity.
- For example, consider a domain model for a person and their passport. Each person can have only one passport, and each passport is associated with only one person.
One-to-Many (1:N) Association:
- In a one-to-many association, one instance of an entity is related to multiple instances of another entity.
- For example, in an e-commerce domain, a customer can place multiple orders. Each order belongs to a single customer, but a customer can have many orders.
Many-to-One (N:1) Association:
- In a many-to-one association, multiple instances of an entity are associated with a single instance of another entity.
- Using the same e-commerce example, multiple orders can be associated with a single customer. Each order has one customer, but a customer can have many orders.
Many-to-Many (N:N) Association:
- In a many-to-many association, multiple instances of an entity are related to multiple instances of another entity.
- For example, in a social media domain, users can have multiple friends, and each friend can have multiple users as friends. This results in a many-to-many association between users.
- association graphical notation